The views expressed in this paper are those of the writer(s) and are not necessarily those of the ARJ Editor or Answers in Genesis.
Abstract
A major shift in thinking seems to be occurring in contemporary evangelical thinking. Southern Baptists overwhelmingly rejected the views of twentieth-century liberal Southern Baptist professors in favor of a literal translation of Genesis. Now, however, this debate may not be so one-sided among Southern Baptists. Within the current evangelical community there is a belief that the age of the earth has no bearing upon the doctrine of inerrancy. A study was conducted in 2013 that reveals belief in the age of the earth is one factor that contributes to the degree to which the doctrine of inerrancy is affirmed. The research revealed that there is a strongly held belief by young-earth creationists and old-earth creationists that the Bible is the inerrant Word of God. However, from inside this belief is a debate between the supremacy of the Bible and the supremacy of science.
Keywords: Southern Baptists, old-earth creationists, young-earth creationists, inerrancy
Introduction
When Crawford Toy, professor at Southern Baptist Theological Seminary in the nineteenth century, taught that the early chapters of Genesis were historically inaccurate (Bush and Nettles 1999) and Elliot’s commentary, published in 1969, questioned the historical accuracy of Genesis (James 1986), Southern Baptists overwhelmingly rejected their views and ensured that the Scriptures were regarded as they intended—the inerrant Word of God.
Historically, Baptists have been a people of the Bible. Robert G. Torbet, in his book A History of the Baptists, summarizes: “Baptists, to a greater degree than any other group, have strengthened the protest of evangelical Protestantism against traditionalism. This they have done by their constant witness to the supremacy of the Scriptures” (Torbet 1963, p. 483). Since the sixteenth century, under the influence of Balthasar Hubmair, Baptists have confirmed the supremacy of the Scriptures. Affirmations of the Scriptures through the London Confession of 1644, Declaration of Faith of 1742, and New Hampshire Confession of 1830 have all revealed the importance the Bible has had for Baptists. The prominence of the Bible has continued within the Southern Baptist Convention with the formulation of The Baptist Faith and Message 1925, The Baptist Faith and Message 1963, and most recently The Baptist Faith and Message 2000. Each time the Southern Baptist Convention fine-tuned their message of faith, they had a goal of elevating the Bible to its rightful position—as the supreme, authoritative, and inerrant Word of God.
Purpose of the Article
Kurt Wise, Professor of Biology at Truett-McConnell College in Georgia and Ph.D. in geology from Harvard University was cited in the Florida Baptist Witness regarding the topic of inerrancy and old-earth theology, and remarked, “Believing in a young earth is in no way a requirement for salvation, however, I do believe, that it is impossible to consistently believe in both an old earth and inerrant scripture” (Roach 2010). Dr. Albert Mohler, President of Southern Baptist Theological Seminary, was quoted in the same article affirming, “Christians who seek to be theistic evolutionists are in the awkward position of trying to adopt a cosmology that has theological ramifications that, in my view, do nothing less than catastrophic damage to the Gospel” (Roach 2010). He adds, “Theologically, the historical Adam as the common ancestor of the human race is the most important issue. But the question is how in the world do you end up with an historical Adam if you have an old earth? It’s becoming increasingly clear that an old earth implies something other than an historical Adam” (Roach 2010).
Do Wise and Molher’s comments reflect a similar belief that the current general membership within the Southern Baptist Convention share as well? Do Southern Baptists affirm a young or old earth interpretation of Genesis 1–11, and how does that influence their understanding of the rest of the Bible? Do Southern Baptists believe in the supremacy of the Bible or the supremacy of science? To date, there has been limited research that reveals what Southern Baptists believe regarding the age of the earth and what influence that belief has upon the belief in the inerrancy of the Bible. This article argues that evolutionary science has influenced a segment of Southern Baptists to doubt the inerrancy of the Bible. Those who believe in old-earth creationism have given greater allegiance to the supremacy of science than the supremacy of the Bible, and even those who affirm young-earth creationism have capitulated to affirm inconsistent beliefs. This argument for an allegiance to a belief in evolutionary science is derived from a statistically significant cluster of factors that have influenced adversely the belief in the doctrine of inerrancy. That is, one’s belief of the authenticity of the Genesis 1–11 biblical account contributes in part to how one views the authority, inerrancy, and sufficiency of Scripture. However, before exploring the data, a brief overview of the Southern Baptists’ understanding of Genesis 1–11 and belief in inerrancy of Bible provides the historical framework of this important issue.
Southern Baptist Affirmation of the Historicity of Genesis 1–11
The Southern Baptist Convention began in 1845 (James 1986), but not until 1925 was there a comprehensive confession of faith (Garrett 2009). The reason for such an absence was not that the newly formed convention did not affirm the supremacy of the Bible; rather, it was because of the Baptists’ aversion to creeds. Their “creed” was “nothing but the Bible” (Garrett 2009, p. 434). A challenge within the Southern Baptist Convention arose in 1876 when Crawford H. Toy, professor at Southern Baptist Seminary, announced that the Bible was simply historically wrong about the Genesis 1–11. He denied the Creation account of Genesis and Noah’s global Flood, and he believed that “Abraham received his monotheism from some existing human source in Chaldea” (Bush and Nettles 1999, p. 211) rather than from divine revelation. Toy eventually resigned and the board accepted his resignation. “The next day . . . several other Baptist state papers carried the announcement . . . [with] expressed deep regret at the loss of Toy, but went on to affirm that is was manifestly right for him to submit his resignation and that it was right for the trustees to accept it” (Bush and Nettles 1999, p. 217).
Toy’s beliefs had compromised the long standing position of the Southern Baptist Convention regarding the Bible and even though there was no official declaration, all involved knew he had denied a deeply held belief of Southern Baptists. Due to “prevalence of naturalism, the continuing agitation over the question of evolution and the fundamentalist-modernist controversy” (Garrett 2009, p. 442), the Baptist Faith and Message 1925 was formed and the following regarding the Bible was affirmed:
We believe that the Holy Bible was written by men divinely inspired, and is a perfect treasure of heavenly instruction; that it has God for its author, salvation for its end, and truth, without any mixture of error, for its matter; that it reveals the principles by which God will judge us; and therefore is, and will remain to the end of the world, the true center of Christian union, and the supreme standard by which all human conduct, creeds and religious opinions should be tried. (Southern Baptist Convention 2013).
In 1961, the Fundamentalists and modernist controversy surfaced again with the Southern Baptist Convention. It swirled around the publication of Ralph Elliot’s commentary of Genesis (Williams 2000, p. 21). Broadman Press (publishing arm of the Southern Baptist Convention) had published Elliot’s commentary, The Message of Genesis, in which he denied the unique creation of Adam and Eve, affirmed Noah’s Flood was local, and the patriarchs were not literal persons (Williams 2000, p. 22). “To make matters worse, Elliot’s employer, Midwestern Baptist Theological Seminary during this controversy, reaffirmed him a consecrated Christian, a promising scholar, and teacher, a loyal servant of the Southern Baptists” (Williams 2000, p. 23). As a result, the Baptist Faith and Message 1963 was adopted with a reaffirmation of the infallibility of Scripture and additional changes designed to “establish doctrinal parameters for all Southern Baptist institutions” (Williams 2000, p. 24). The implication was that Elliot’s commentary was unacceptable language to describe the belief that the Holy Bible was written by men, divinely inspired, and is a perfect treasure of divine instruction without any mixture of error.
The controversy did not end in 1963; rather, it escalated in 1969 when Broadman Press published the Broadman Commentary and choose G. Henton Davies to comment on Genesis. His beliefs were no different than Elliot’s regarding the historical accuracy of Genesis (Williams 2000, p. 25). This revealed that the leadership within the Southern Baptist Convention held different views of the inspiration of the Bible than the intended understanding of the Baptist Faith and Message of 1925 and 1963. “For the first time in several decades Southern Baptists faced a theological crisis” (Bush and Nettles 1999, p. 328). A resurgence of the supremacy of the Bible was needed. Two conservative men, who believed in the inerrancy of the Bible, Paige Patterson and a Federal judge from Houston, Paul Pressler, had an idea on how to reverse the liberalism that had penetrated the Southern Baptist Convention leadership.
Influence of International Council of Biblical Inerrancy on Southern Baptist Convention
During the same time of the Southern Baptist Convention resurgence, the International Council of Biblical Inerrancy was birthed in 1977 with the expressed intent to “support the historical view on inerrancy” (Geisler and Roach 2011, p. 25). A group of men led by R. C. Sproul drafted an article expressing a theological understanding of the term inerrancy (Geisler and Roach 2011). One year later a group of 240 signatories out of 268 participates representing leadership of various streams of evangelicalism produced the Chicago Statement on Biblical Inerrancy. The Chicago Statement of 1978 expressed a short declaration on inerrancy that the autographic text of the Scripture is the inspired and the inerrant Word of God (Bush and Nettles 1999, p. 332). Included with the short statement were 19 articles affirming the definition of inerrancy, and an official commentary (Sproul 1996). Three prominent Southern Baptist Convention leaders signed the statement—Russ Bush, W. A. Criswell, and Paige Patterson. The influence of the Chicago Statement on the Southern Baptist Convention was so significant that one of the signees—Russ Bush—proposed that the Southern Baptist Convention adopt the statement as its model. His proposal was a significant factor leading to the formation of the Baptist Faith and Message 2000.
Resurgence of the Southern Baptist Convention
Turbulent times over the Elliot commentary in 1961 and the publication of the Broadman Commentary in 1969 coupled with “double speak”—adroit speech in which seminary professors spoke in such a way that simple layman heard a straight forward interpretation of the Bible while at the same time the professor would affirm modern biblical criticism of the Bible that only sophisticated hearers could understand—caused consternation for the conservatives within the Southern Baptist Convention. “The Southern Baptist seminary classroom of that day had little sympathy with the traditional beliefs of most Baptists in the churches in the present or with the theology of Baptist theologians in the past” (Bush and Nettles 1999, p. 335). To reverse this trend, conservatives, led by Paige Patterson and Paul Pressler, came up with a plan whereby they would win back the seminaries and denominations. The plan was to recruit delegates who would elect presidents for the Southern Baptist Convention who affirmed inerrancy. In turn, the presidents would appoint persons to central positions within the denomination, who, in turn, would appoint board members to the seminaries. The board members would elect seminary presidents who affirmed inerrancy, and then these presidents would hire deans and faculty who affirm the doctrine of inerrancy (Bush and Nettles 1999; Garrett 2009; Geisler and Roach 2011; Williams 2000). In short, a conservative resurgence of the fundamental belief in the inerrancy of the Bible would be restored to the Southern Baptist Convention if Patterson and Pressler had their way.
The plan was successful and, in 1979, Adrian Rodgers was elected president with 55% of the vote (Williams 2000, p. 58). This process continued through 1985 with successive election of Southern Baptist Convention presidents who affirmed inerrancy of the Bible, yet this created controversy within the convention and peace needed to be made between conservatives and moderates/liberals. In 1985, a Peace Committee was formed to “determine the sources of the controversy and make findings and recommendations . . . so that Southern Baptists might affect reconciliation” (Bush and Nettles, 1999, p. 496). The Peace Committee made its final report in 1987 at the Southern Baptist Convention in St. Louis and found that a liberal drift had entered the convention. They found evidence of a mixture of beliefs. Within the six seminaries there were diversity of opinions from the faculty members, who affirmed or modified the historicity of Adam, the historical events in the Bible, the authorship of every book of the Bible, and the miracle claims reported in the Bible (Report of the Southern Baptist Convention Peace Committee 1987). Two recommendations were made: 1) “acceptance that the seminaries were the root of the problem in the convention” and 2) “any solution to the controversy must be rooted in a plan to change the seminaries” (Williams 2000, pp. 138–139).
Prior to St. Louis, the Peace Committee met at the Glorieta Baptist Conference Center near Santa Fe, New Mexico (1986), where the six seminary presidents vowed to affirm the full inspiration of Bible. The declaration was known as the Glorieta Statement which affirmed “Christianity is supernatural in its origin and history,” “miracles of the Old and New Testament are historical,” and “the sixty-six books of the Bible are not errant in any area of reality” (Report of the Southern Baptist Convention Peace Committee 1987). This was considered a victory for the conservative resurgence and ensured continuation of Southern Baptist Convention presidents who would affirm the inerrancy of the Bible.
The inerrancy movement continued within the Southern Baptist Convention, and, in 1999, a majority of the Southern Baptist messengers, who were not satisfied with the complete wording of the Baptist Faith and Message 1963, asked for a blue ribbon panel to review and make recommendations (Garrett 2009, p. 506). T. C. Pinckney of Virginia made a motion to incoming president Paige Patterson to revisit the 1963 Baptist Faith and Message (Wooddell 2007). The result was the formation of the Baptist Faith and Message Committee. There were 14 committee members including Richard Land, R. Albert Mohler, Jerry Vines, and Adrian Rogers. The committee returned the following year at the annual convention in Orlando and their recommendations formed the changes that created the BFM 2000.
Major changes were made in sections with the wording of the Scripture, the triunity of God, the omniscience of God, the humanity and deity of Jesus, the exclusivity of the Gospel, and the roles of men and women. Within the area of Scripture, the phrases “therefore, all Scripture is totally true and trustworthy” (Wooddell 2007, sec. 467) and “all Scripture is a testimony to Christ, who is Himself the focus of divine revelation” (Wooddell 2007, sec. 467) were added, and the phrase “the criterion by which the Bible is to be interpreted is Jesus Christ” (Wooddell 2007, sec. 467) was removed. The conservatives had won and had articulated what the Southern Baptist Convention had collectively affirmed since their inception and what moderate and liberals had desired to erode—the supreme authority in the error-free Word of God called the Bible.
Knowing that the leadership of the Southern Baptist Convention had affirmed inerrancy and had elevated the plain meaning of Genesis 1–11 was the primary purpose. The secondary and tertiary purposes were to revitalize the six seminaries with professors that would affirm the BFM 2000 with a result that the general membership of Southern Baptist Convention, in time, would affirm the BFM 2000 as well. In 2013, this researcher sampled a population of Florida Southern Baptist members to ascertain to what degree, if any, they affirm the doctrine of inerrancy. The process to gather and analyze the data will be discussed next.
Research Process
The Southern Baptist Convention has a membership of over 16,000,000 (Southern Baptist Convention 2013) and the Florida Baptist Convention has about 1,000,000 (Florida Baptist Convention 2013). Leedy and Ormrod claim that beyond populations of 5000 a sample size of 400 is adequate (2004, p. 217). There were 502 randomly selected participants representing the Southern Baptist Churches of Florida. This provided a 95% confidence level that results were accurate (http://www.surveysystem.com). The researcher developed an assessment tool called the Biblical Inerrancy Test (BIT) consisting of 68 questions: 46 were Likert-scale (quantitative) and 22 were open-ended (qualitative). The validity and reliability of the BIT was determined by an expert panel comprised of faculty and a research firm. The phone calls were made by America’s Research Group. Britt Beemer began America’s Research Group in 1979 as a research and strategic consulting firm. The list of America’s Research Group clients includes many of the nation’s top retailers, leading brands, investors, and entrepreneurial companies. America’s Research Group consumer telephone surveys are conducted by a dedicated, well-trained group of researchers with frequent monitoring and quality-assurance procedures. Results are compiled by their staff of market research professionals (Beemer 2011). America’s Research Group has produced statistical research for Answers in Genesis for two books: Already Gone and Already Compromised.
Age of the Earth Survey Question
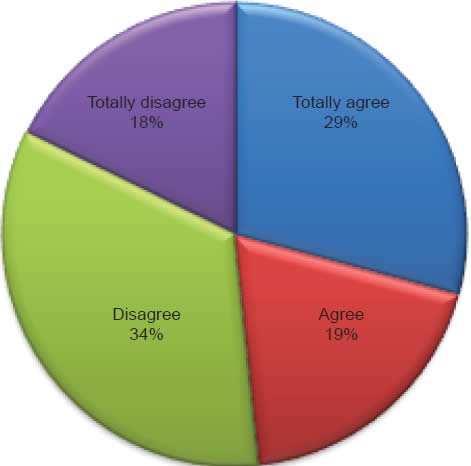
After the results from the Biblical Inerrancy Test were compiled and analyzed the researcher explored the responses of question 31 (Q31). The purpose in this question was to discover to what degree Florida Southern Baptists affirm a belief in the age of the earth based upon the current influence of evolutionary science and teaching of the Bible. The question and results are outlined below.
Of the 502 Florida Southern Baptist church members surveyed, the highest response rate was Disagree at 34%.2 The second highest response rate was Totally agree at 29% and this was followed by Agree at 19%, and then Totally disagree at 18%. There was one missing response that accounted for 0.2%. To state in a slightly different way 48% (adding Totally agree and Agree together) believe the earth was less than 12,000 years old and 52% (adding Disagree and Totally agree together) believe the earth is more than 12,000 years old. From this point forward they will be called young-earth creationists and old-earth creationists. Although the reader will discover quickly that respondents who identify as Southern Baptist in Florida do not consistently affirm their beliefs.3 This will be similar to those who claim to hold to inerrancy but inconsistently affirm this doctrine by denying various historical events in the Bible. The goal is not to make final judgments on who is an inerrantist or young- or old-earth creationist, rather to show the influence of evolutionary science upon the belief of inerrancy within a segment of the Southern Baptist Convention.
Discovering that roughly 50% affirm a young-earth belief and 50% affirm an old-earth belief the researcher wanted to determine how these two groups, when accentuated, answered the remaining 67 questions of the BIT.4 Namely, do those who affirm a young earth or an old earth answer inerrancy related questions differently? The following tables reveal how old-earth creationists and young-earth creationists answered the questions from the Biblical Inerrancy Test.
Beliefs of Young-Earth and Old-Earth Creationists
Chart 2
Q1. Do you feel all the accounts/stories in Bible are true?
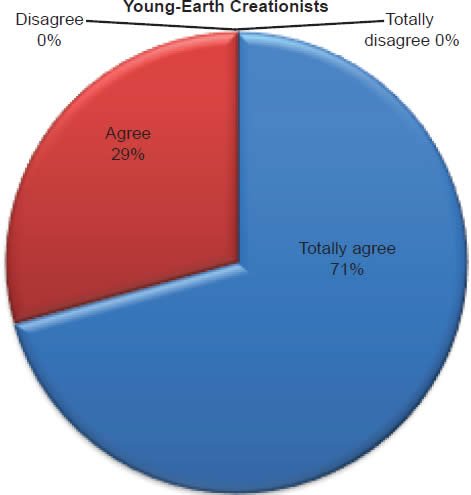
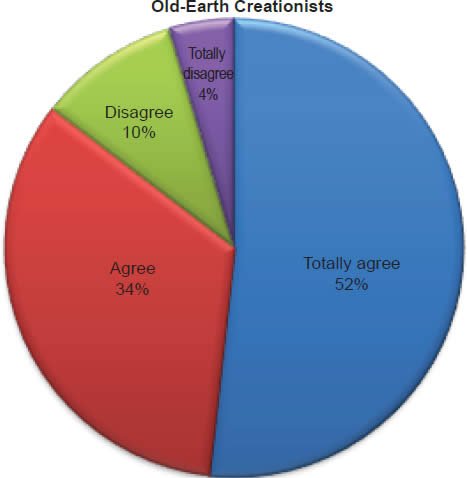
The question was asked “Do you feel all the accounts/stories in the Bible are true?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0%5 either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 86% either Totally agree or Agree and 14% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 3
Q4. Do you feel Bible is true and trustworthy in all matters?
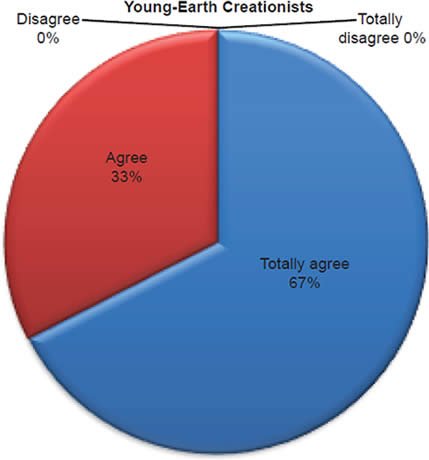
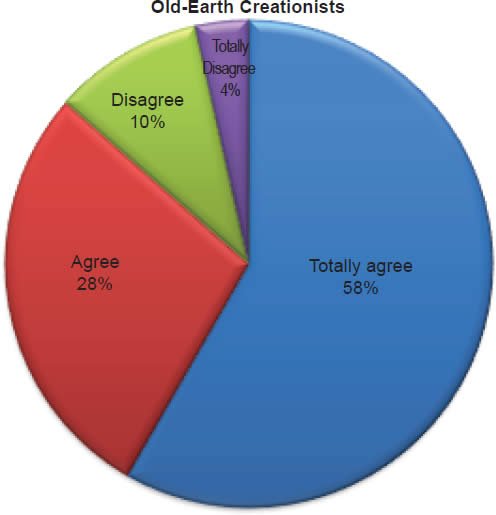
The question was asked “Do you feel Bible is true and trustworthy in all matters?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0%5 either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 87% either Totally agree or Agree and 14% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 4
Q7. Do you feel Bible contains errors?
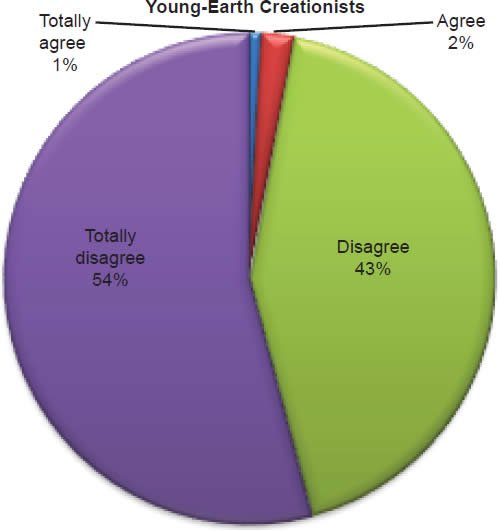
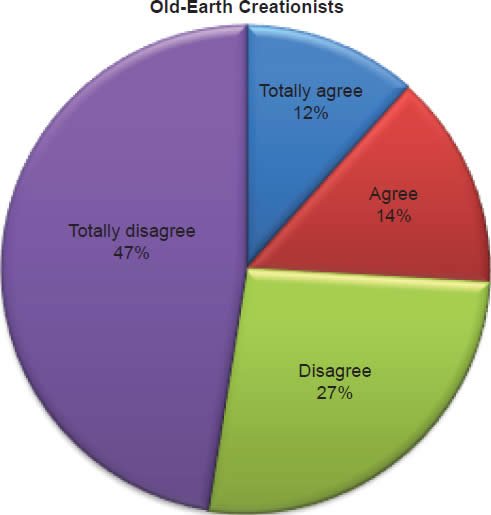
The question was asked “Do you feel Bible contains errors?” The responses were 3% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 97% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 26% either Totally agree or Agree and 74% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 5
Q12. Do you feel the doctrine of Trinity is taught in the Bible?
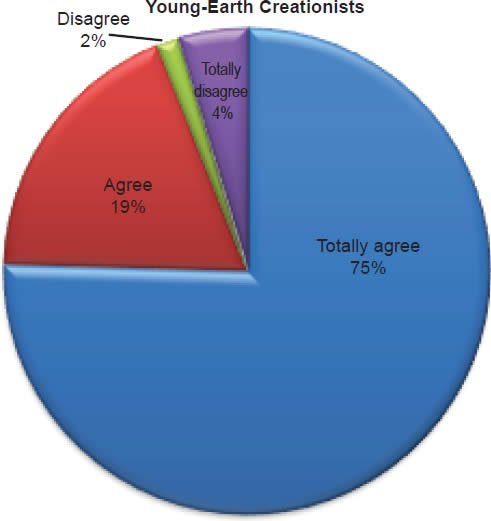
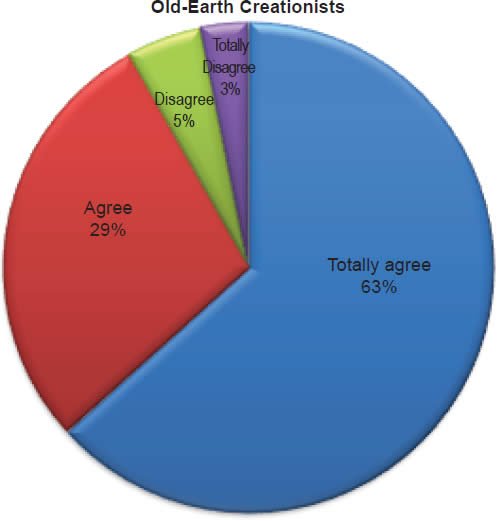
The question was asked “Do you feel the doctrine of Trinity is taught in the Bible?” The responses were 94% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 6% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 92% either Totally agree or Agree and 8% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 6
Q17. Do you feel Jesus died by crucifixion on a cross?
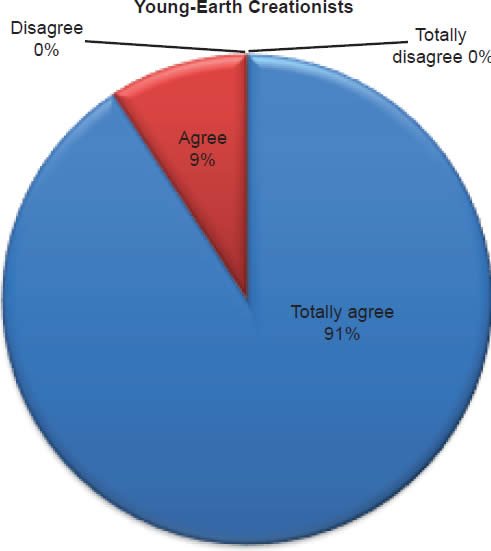
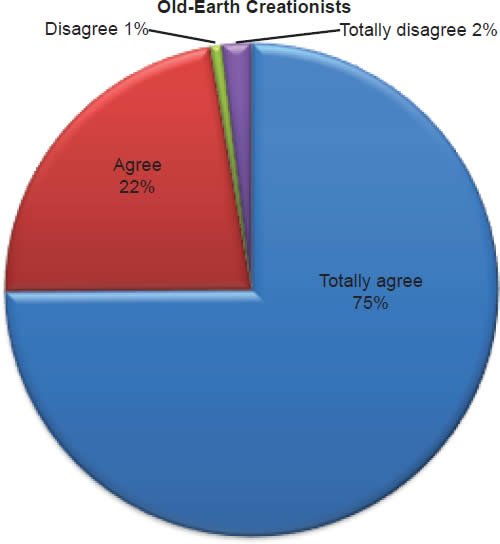
The question was asked “Do you feel Jesus died by crucifixion on a cross?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 97% either Totally agree or Agree and 3% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 7
Q20. Do you feel Jesus rose from the dead after three days in the grave?
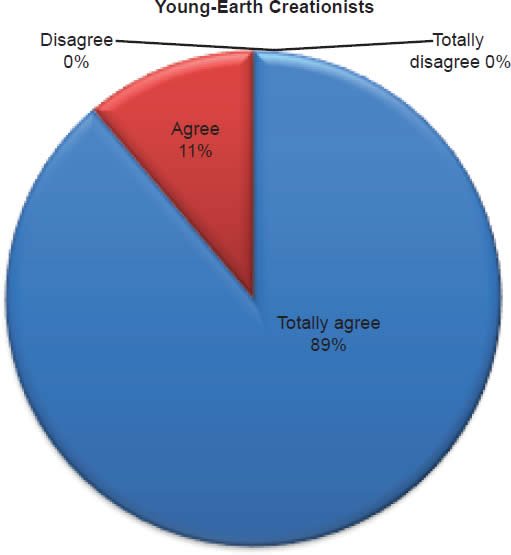
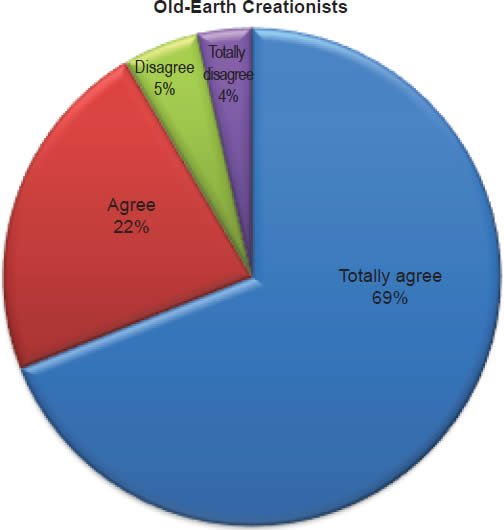
The question was asked “Do you feel Jesus rose from the dead after three days in the grave?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 91% either Totally agree or Agree and 9% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 8
Q25. Do you feel Jonah was inside a whale/fish for three days?
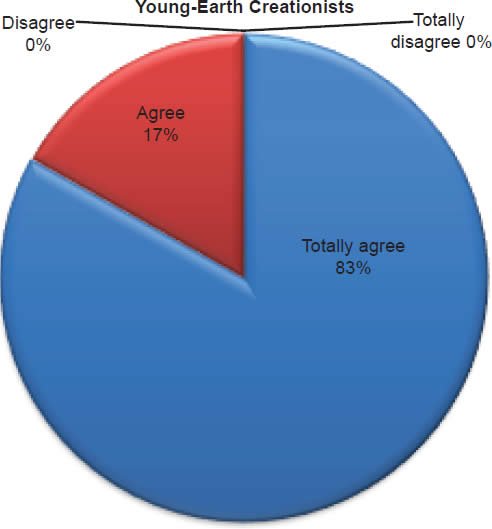
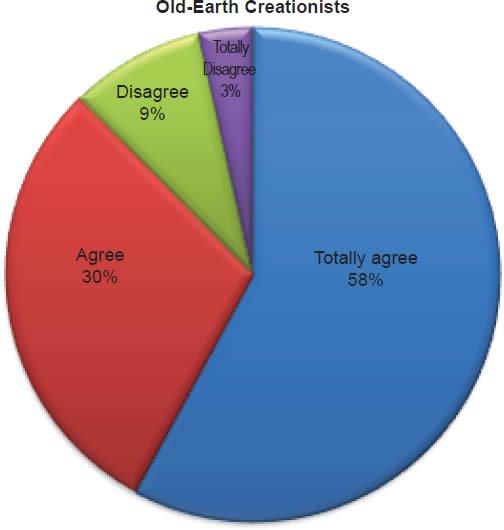
The question was asked “Do you feel Jonah was inside a whale/fish for three days?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 88% either Totally agree or Agree and 12% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 9
Q26. Do you feel Daniel was thrown into a pit with lions and was not hurt?
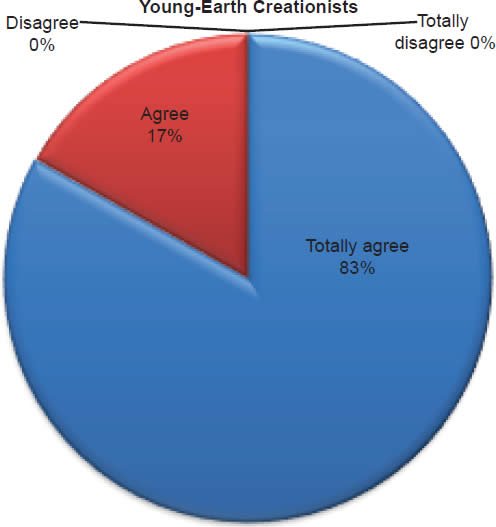
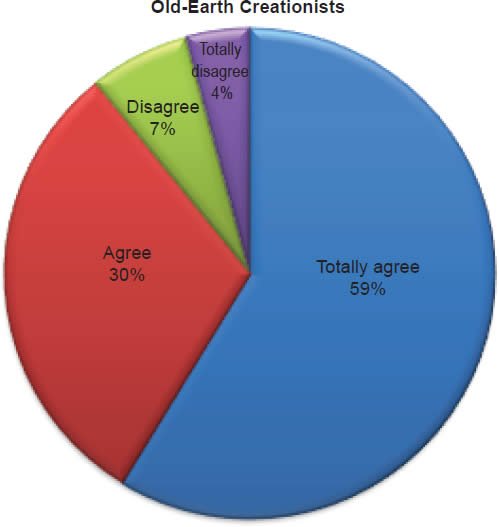
The question was asked “Do you feel Daniel was thrown into a pit with lions and was not hurt?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 89% either Totally agree or Agree and 11% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 10
Q28. Do you feel Moses parted the Red Sea and Israel walked on dry ground?
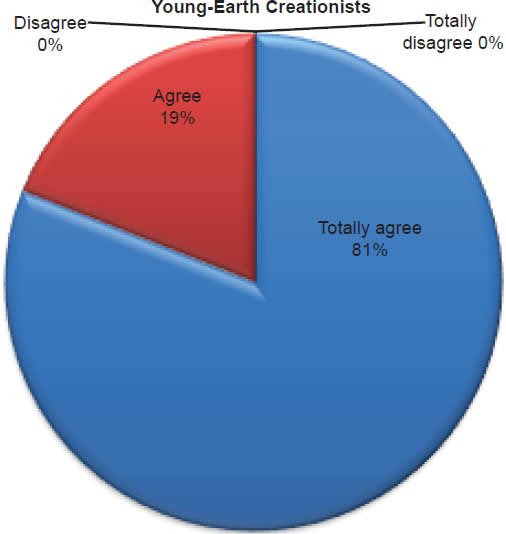
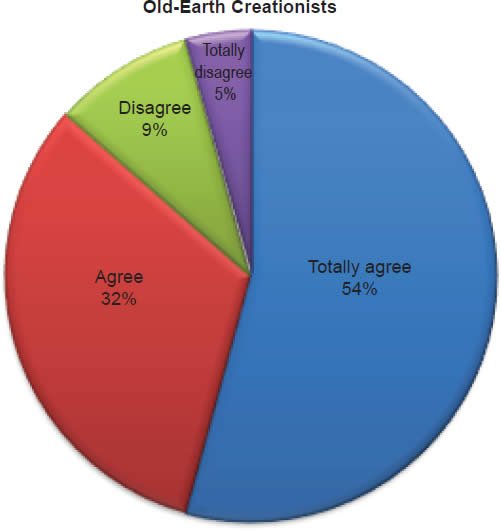
The question was asked “Do you feel Moses parted the Red Sea and Israel walked on dry ground?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 86% either Totally agree or Agree and 14% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 11
Q33. Do you feel God created the earth in six literal 24-hour days?
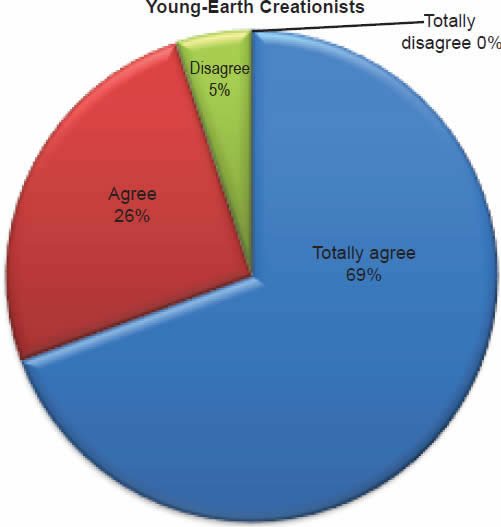
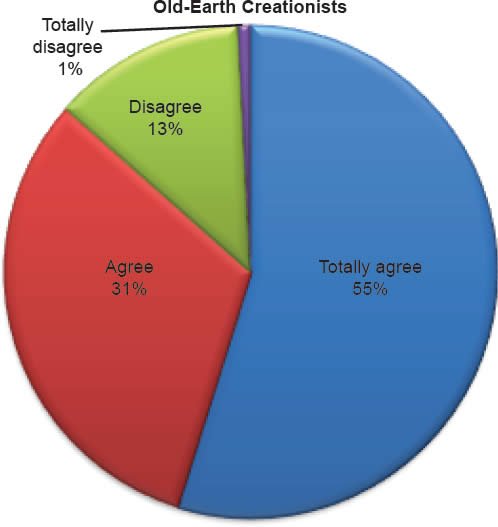
The question was asked “Do you feel God created the earth in six literal 24-hour days?” The responses were 95% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 5.0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 86% either Totally agree or agree and 14% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 12
Q34. Do you feel Adam and Eve were real people?
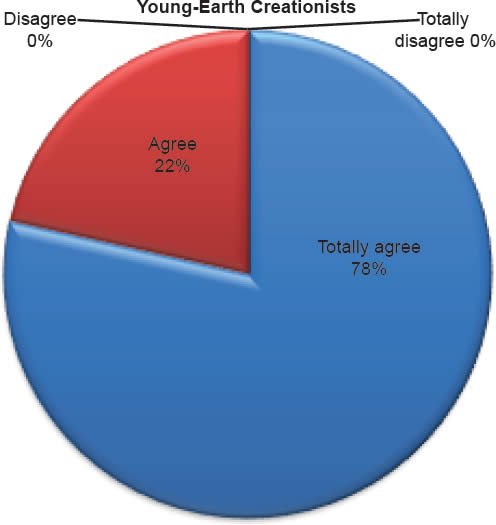
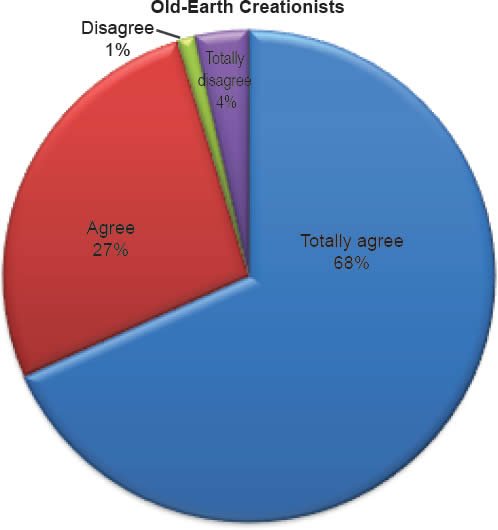
The question was asked “Do you feel Adam and Eve were real people?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 95% either Totally agree or Agree and 5% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 13
Q35. Do you feel dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago?
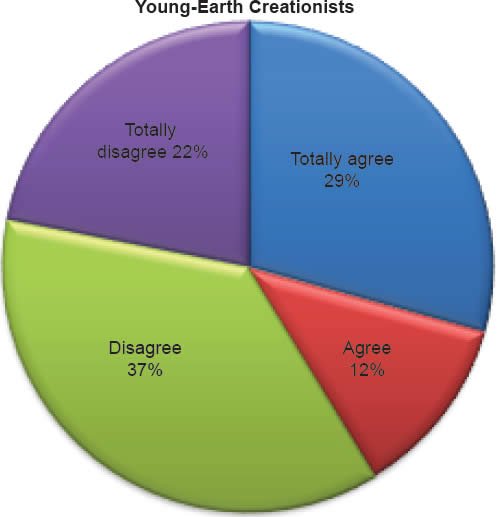
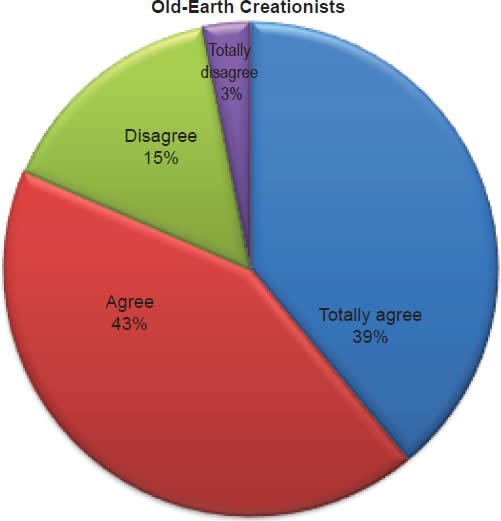
The question was asked “Do you feel dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago?” The responses were 41% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 59% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 82% either Totally-agree or Agree and 18% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 14
Q40. Do you feel humans evolved from ape-like creatures?
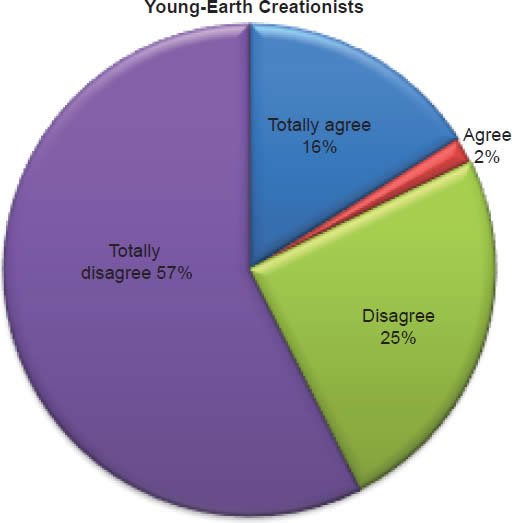
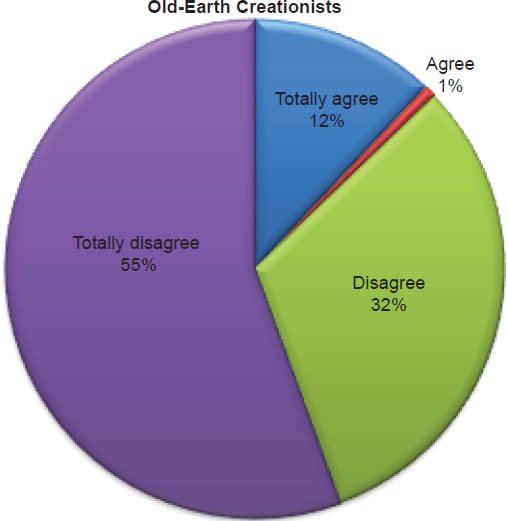
The question was asked “Do you feel humans evolved from ape-like creatures?” The responses were 18% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 82% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 13% either Totally agree or Agree and 87% either Disagree or Totally disagree.6
Chart 15
Q41. Do you feel because of science that the earth is millions/billions of years old?
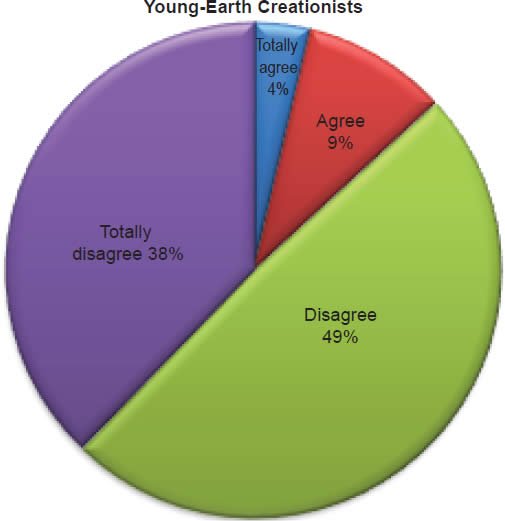
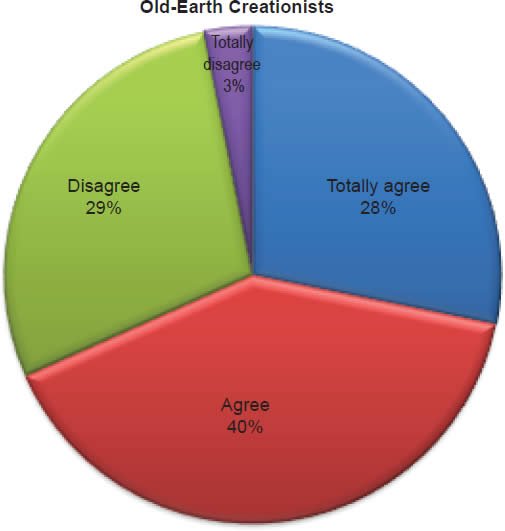
The question was asked “Do you feel because of science that the earth is millions/billions of years old?” The responses were 13% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 87% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 68% either Totally agree or Agree and 32% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 16
Q44. Do you feel there was a global Flood during the days of Noah?
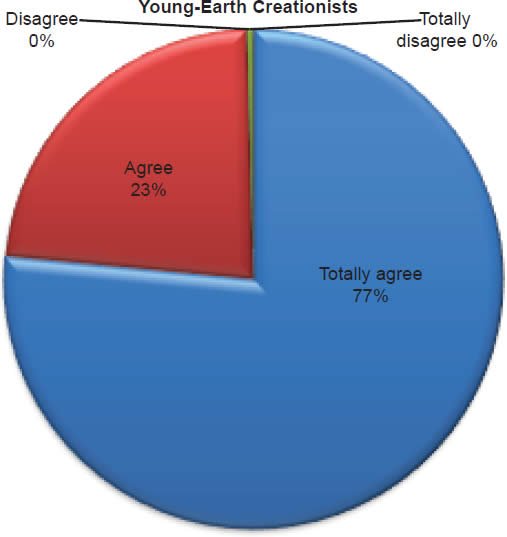
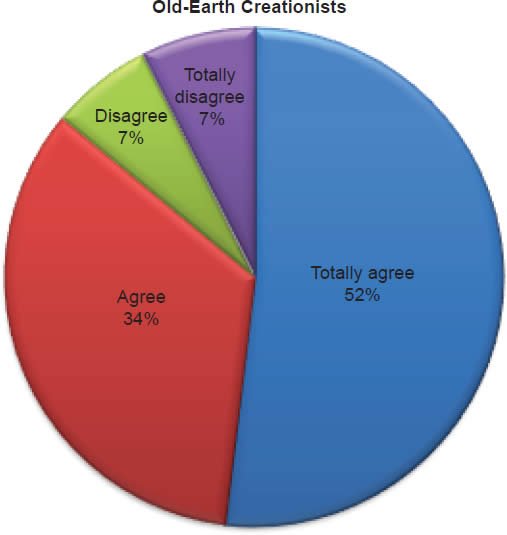
The question was asked “Do you feel there was a global Flood during the days of Noah?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 86% either Totally agree or Agree and 14% either Disagree or Totally disagree.7
Chart 17
Q45. Do you feel Noah and his family were the only humans to survive the Flood?
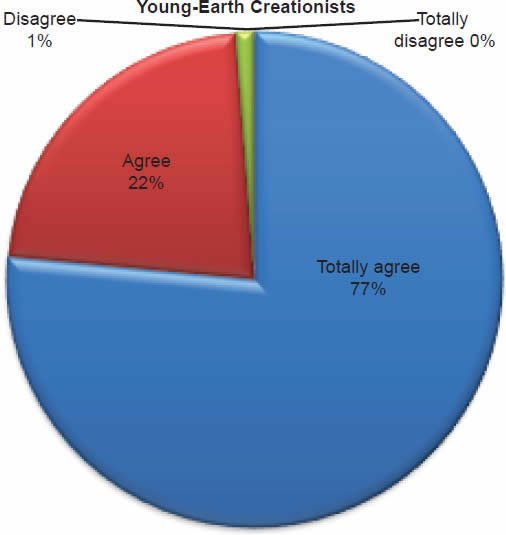
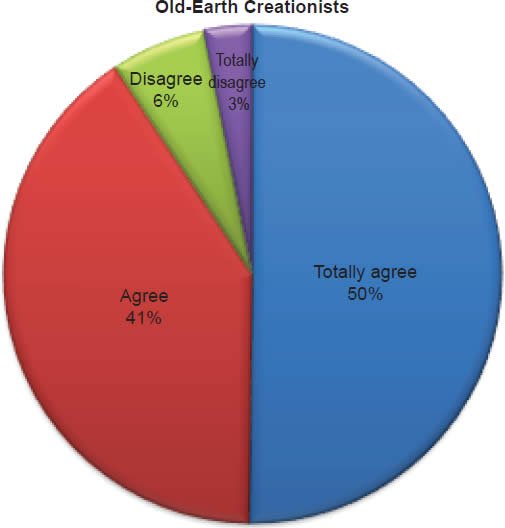
The question was asked “Do you feel Noah and his family were the only humans to survive the Flood?” The responses were 99% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 1% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 91% either Totally agree or Agree and 9% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 18
Q23. Do you feel Jesus is coming back?
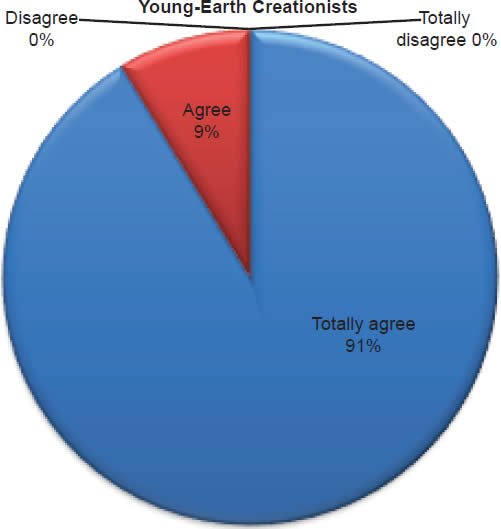
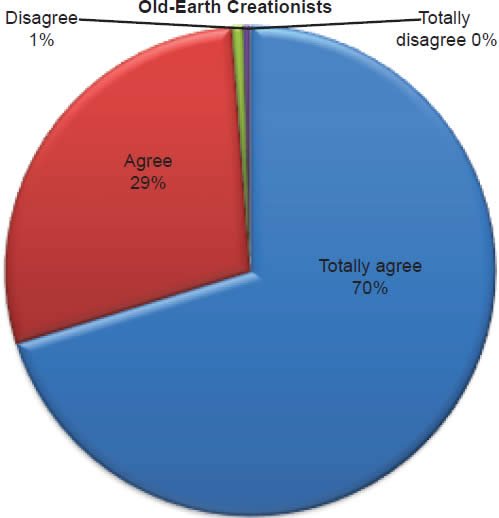
The question was asked “Do you feel Jesus is coming back?” The responses were 100% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 0% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 99% either Totally agree or Agree and 1% either Disagree or Totally disagree.8
Chart 19
Q49. Do you feel the Bible is the final authority in my life when I make decisions?
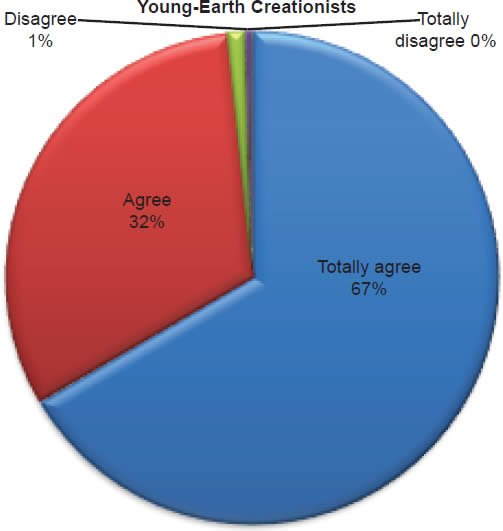
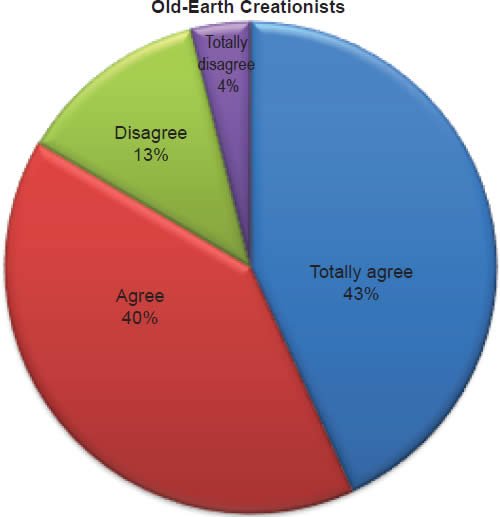
The question was asked “Do you feel the Bible is the final authority in my life when I make decisions?” The responses were 99% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 1% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 83% either Totally agree or Agree and 17% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 20
Q50. Do you feel homosexual marriage is a biblically acceptable lifestyle?
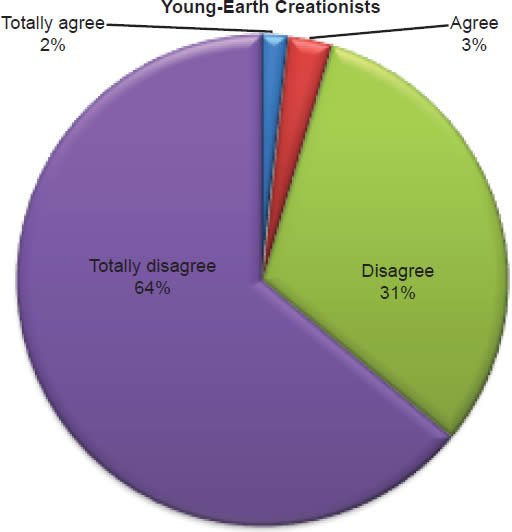
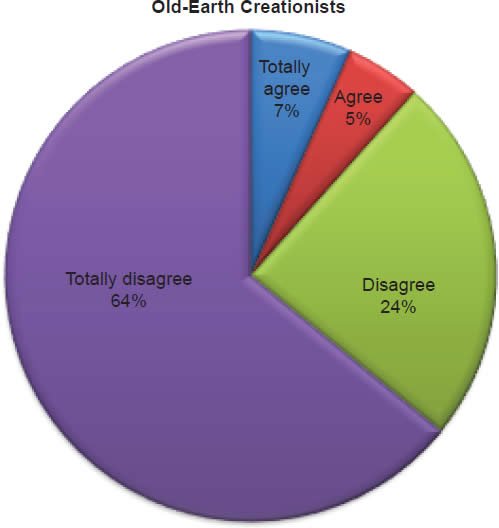
The question was asked “Do you feel homosexual marriage is a biblically acceptable lifestyle?” The responses were 5% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 95% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 12% either Totally agree or Agree and 88% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 21
Q53. Do you feel abortion is acceptable?
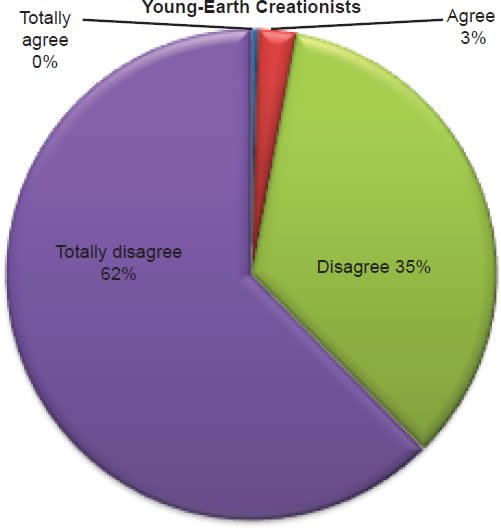
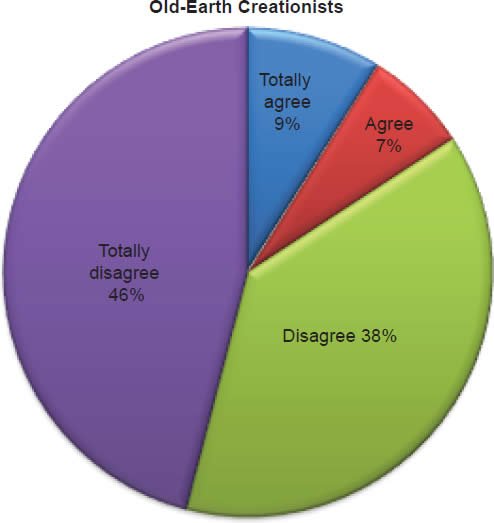
The question was asked “Do you feel abortion is acceptable?” The responses were 3% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 97% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 16% either Totally agree or Agree and 84% either Disagree or Totally disagree.9
Chart 22
Q57. Do you feel living with your girl/boyfriend before marriage is acceptable?
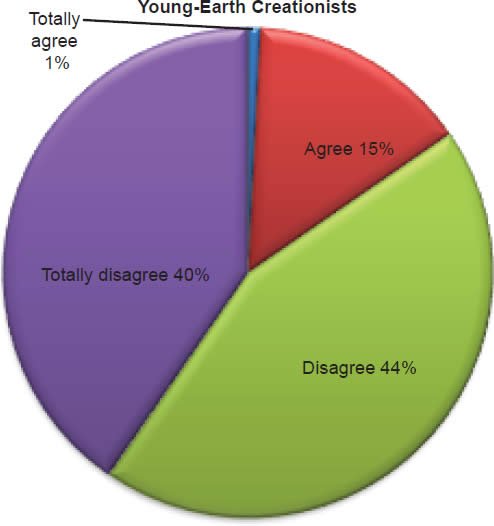
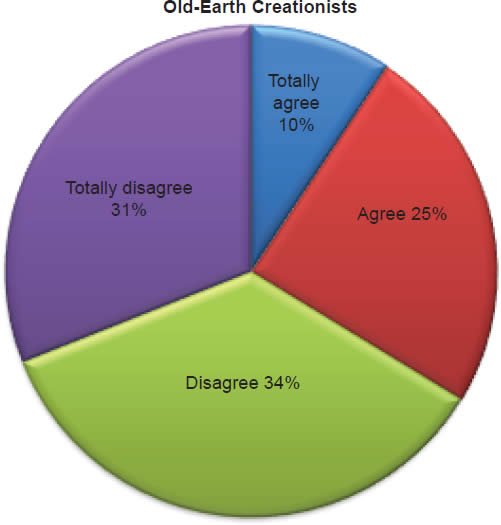
The question was asked “Do you feel living with your girl/boyfriend before marriage is acceptable?” The responses were 16% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 84% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 34% either Totally agree or Agree and 66% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 23
Q58. Do you feel a Christian marrying a non-Christian is acceptable to the Bible?
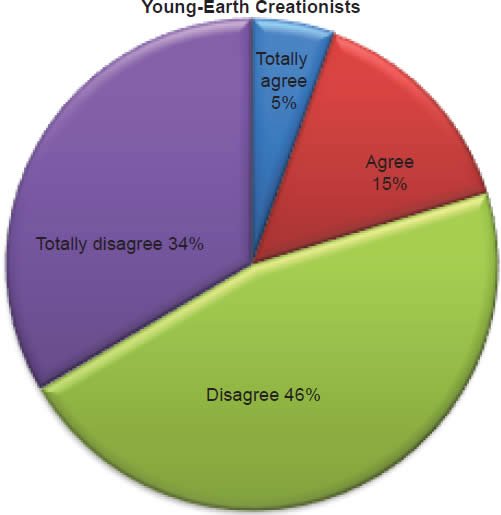
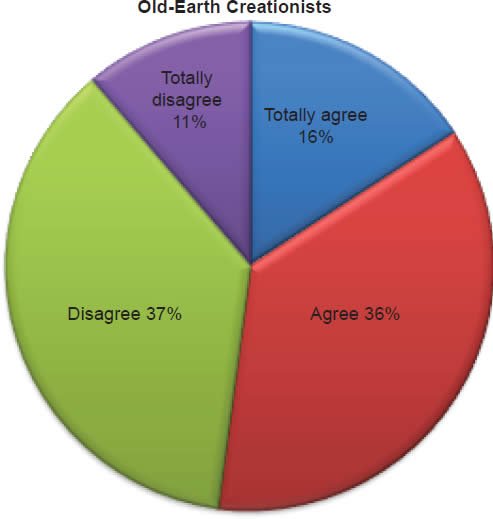
The question was asked “Do you feel a Christian marrying a non-Christian is acceptable to the Bible?” The responses were 20% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 80% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 52% either Totally agree or Agree and 48% either Disagree or Totally disagree.
Chart 24
Q62. Do you feel the Bible permits women to be pastors just like men?
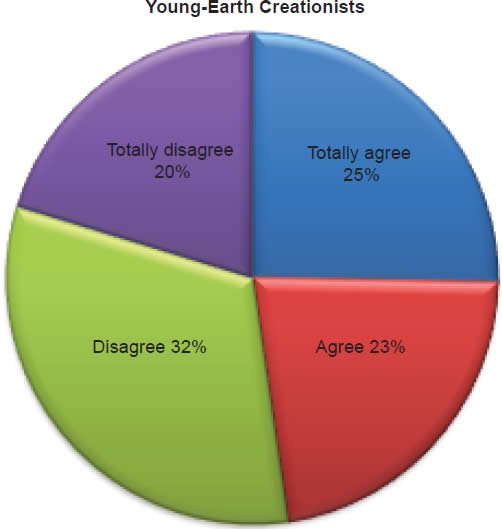
The question was asked “Do you feel the Bible permits women to be pastors just like men?” The responses were 48% of young-earth creationists either Totally agree or Agree and 52% either Disagree or Totally disagree. Of the old-earth creationists 43% either Totally agree or Agree and 57% either Disagree or Totally disagree.10
Demographics of Florida Southern Baptists
Chart 25
Q64. How often do you attend your church?
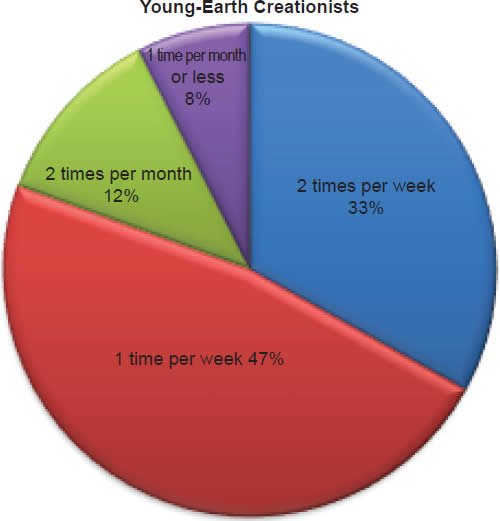
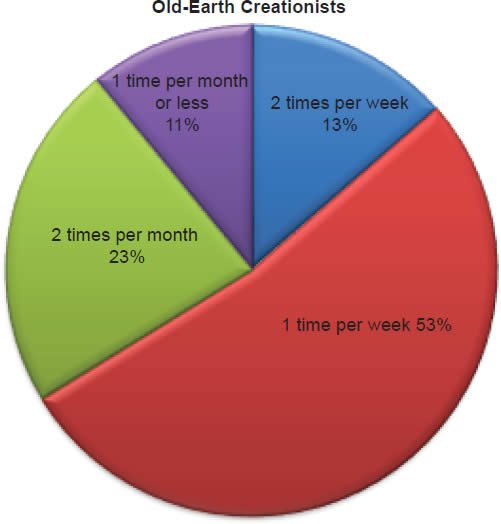
The question was asked “How often do you attend your church?” Of young-earth creationists 33% attend two times or more per month, 47% attend one time per week, 12% attend two times per month, and 8% attend one time or less per month. Of old-earth creationists 13% attend two times or more per month, 53% attend one time per week, 23% attend two times per month, and 11% attend one time or less per month.
Chart 26
Q65. How often do you read your Bible?
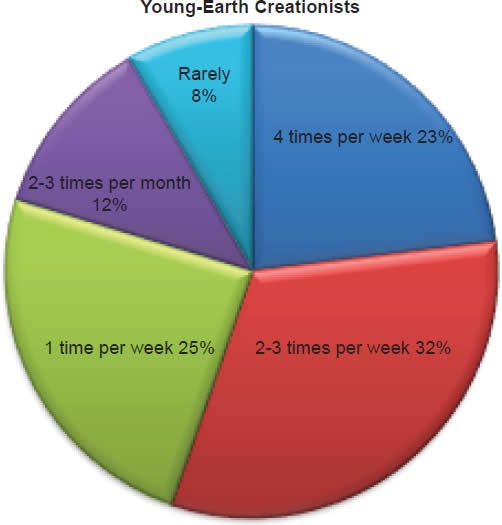
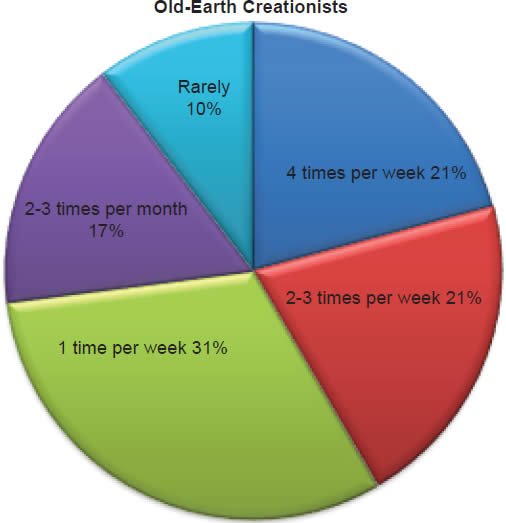
The question was asked “How often do you read your Bible?” Of young-earth creationists 23% read four times (or more) per week, 32% read two to three times per week, 25% read one time per week, 12% read two to three times per month, and 8% read rarely. Of old-earth creationists 21% read four times (or more) per week, 21% read two to three times per week, 31% read one time per week, 17% read two to three times per month, and 10% read rarely.
Chart 27
Q63. Age Groups
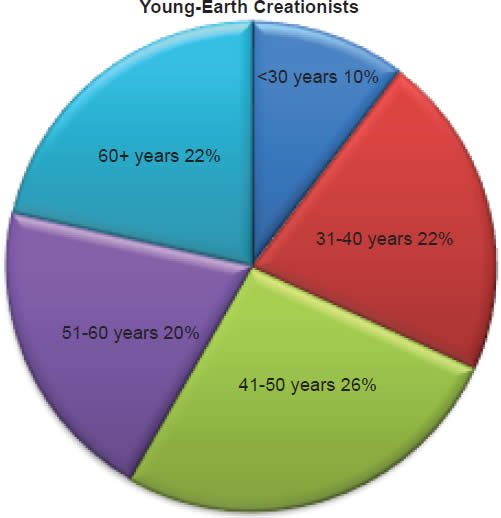
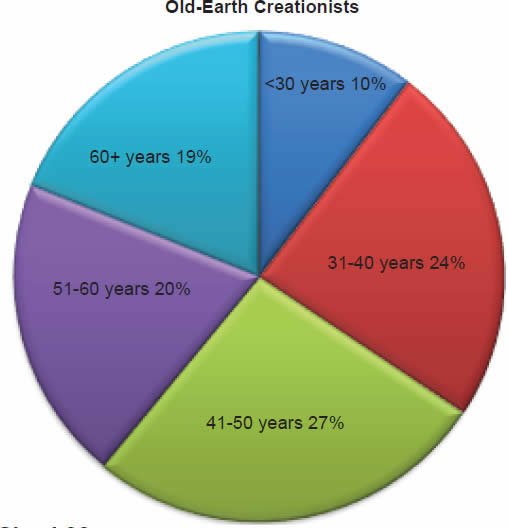
The statement was made, “I’m going to read you a list of age groups. Please stop me when I get to yours.” Of young-earth creationists 10% were 30 years old or younger, 22% were between the ages of 31–40 years old, 26% were between the ages of 41–50 years old, 20% were between the ages of 51–60 years old, and 22% were 60 years or older. Of old-earth creationists 10% were 30 years old or younger, 24% were between the ages of 31–40 years old, 27% were between the ages of 41–50 years old, 20% were between the ages of 51–60 years old, and 19% were 60 years or older.
Chart 28
Q67. Sex/Gender (By observation)
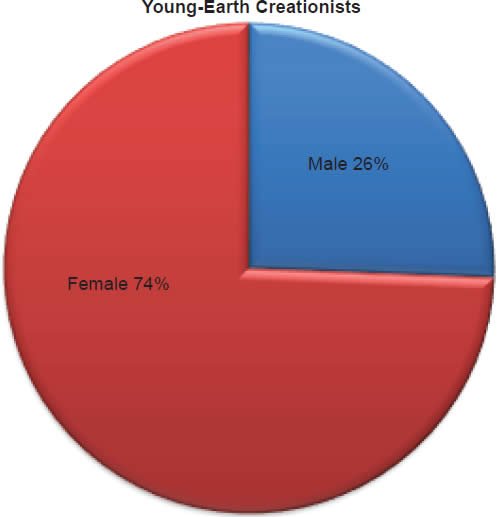
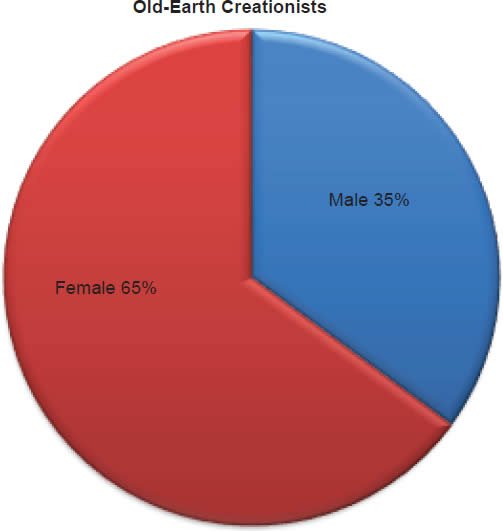
America’s Research Group by voice identification on the phone selected gender. Of the young-earth creationists 26% were identified as male and 74% were identified as female. Of the old-earth creationists 35% were identified as male and 65% were identified as female.
The foregoing data lead to a number of interesting implications and theological reflections. Although the sample population was Florida Southern Baptists, the results may be transferable to other Southern Baptists or evangelical congregations if the church members share similar characteristics and theological beliefs with Florida Southern Baptist members.11 As previously stated, the purpose of this article is to argue that evolutionary science has influenced a segment of Southern Baptists to doubt the inerrancy of the Bible. Those who believe in old-earth creationism have given greater allegiance to the supremacy of science than the supremacy of the Bible, and even those who affirm young-earth creationism have capitulated to affirm inconsistent beliefs. This argument for an allegiance to belief in evolutionary science is derived from a statistically significant cluster of factors that has influenced adversely the belief in the doctrine of inerrancy. That is, one’s belief in the age of the earth contributes in part to how one views the authority, inerrancy, and sufficiency of Scripture. Before addressing the implications and theological reflections, some further statistical analysis is warranted.
Statistical Analysis
A factor analysis12 was computed using SPSS, the leading statistics software for the social sciences, with the initial eigenvalue set at 1. The results revealed that there were ten factors that contributed to understanding the variance of the BIT survey results. Those ten factors had a cumulative percentage of 59.762. That is, those ten factors were able to explain roughly 60% of the variance from the mean. A rotated factor matrix revealed that the ten factors could be condensed into five clusters of factors based upon question similarity.
The researcher labeled the clusters as follows:
Factor #1—Deity of Christ
Q8 Jesus was born of a Virgin.
Q17 Jesus died by crucifixion on a cross.
Q18 Jesus’ dead body was laid in a tomb.
Q19 There were eyewitnesses who saw Jesus after His resurrection.
Q20 Jesus rose from the dead after three days in the grave.
Factor #2—Genesis 1–11
Q31 The earth is less than 12,000 years old.
Q32 Adam and Eve were created about 12,000 years ago or less.
Q37 Evolution is the process that God used to create humans.
Q38 God used evolution to change one kind of animal to another kind.
Q39 Dinosaurs died out before there were people on the planet.
Q40 Humans evolved from ape-like creatures.
Q46 Noah’s Flood was a local flood.
Factor #3—Authority of the Bible for Personal Living
Q49 The Bible is the final authority in my life when I make decisions.
Q50 Homosexual marriage is a biblically acceptable lifestyle.
Q57 Living with your boy/girlfriend before marriage is acceptable.
Q58 A Christian marrying a non-Christian is acceptable to the Bible.
Q62 The Bible permits women to be pastors just like men.
Factor #4—General Affirmation of Inerrancy
Q1 All the accounts/stories in the Bible are true.
Q2 All the books of the Bible are true.
Factor#5—Church Attendance and Bible Reading
Q64 Church attendance
Q65 Bible reading
The importance of this factor analysis is to reveal that even though there was a general affirmation of the inerrancy of the Bible by young- and old-earth creationists of Florida Southern Baptists, those who did not affirm inerrancy consistently did so for various reasons. One of the reasons was their belief (or lack of belief) in the supernatural (origins) events in Genesis 1–11. Evolutionary science has influenced old- and young-earth creationists alike to deviate from the plain meaning of the historical events in Genesis 1–11. Although Genesis 1–11 was only one of the five clusters of factors identified, it was a factor, thus indicating that one’s belief in Genesis 1–11 has a bearing upon one’s viewpoint of inerrancy. Another factor was church attendance and Bible reading, which seems logical to include. Those Florida Southern Baptists who struggle to corporately gather with the body of Christ and daily read God’s Word would understandably be less influenced by the Bible and by default influenced by the current trends of the time, namely, evolutionary science. By considering just two of the five clusters of factors, one can deduce the reasons why some members of the Florida Baptist Convention did not consistently affirm the doctrine of inerrancy.
Implications from the Data
The frequency data in conjunction with the factor analysis shows that there are implications such that belief in the age of the earth is one factor that can influence other inerrancy related beliefs.13 In addition, the other four factors: one’s belief (or disbelief) in the authority of the Bible for personal living; deity of Christ; general affirmation in inerrancy; and one’s church attendance and frequency of Bible reading also contributed to the degree to which Florida Southern Baptist members affirmed inerrancy of the Bible. These analyses lead to a number of conclusions.
Inerrancy (in General)
Belief in the inerrancy of the Bible is strongly affirmed by both groups as represented in Chart 2, Chart 3, and Chart 4, but a small percentage of old-earth creationists have doubts about this key doctrine of the church. With young-earth creationists 0% dispute that all the stories/accounts of the Bible were true, 0% dispute that the Bible is true and trustworthy in all matters, and 3% believe the Bible contains errors. Averaging the percentages together, about 1% of young-earth creationists doubt the inerrancy of the Bible. This is contrasted with old-earth creationists of whom 14% dispute that all the stories/accounts of the Bible were true, 14% dispute that the Bible is true and trustworthy in all matters, and 26% believe the Bible contains errors. Averaging the percentages together, 18% (about 1/6th) of old-earth creationists have doubts about the inerrancy of the Bible.
Doctrine of the Trinity
Belief in the doctrine of the Trinity is very much affirmed as described in Chart 5. With young-earth creationists 6% dispute that the doctrine of the Trinity is taught in the Bible. With old-earth creationists 8% dispute that the doctrine of the Trinity is taught in the Bible. Both percentages are surprisingly high and with the margin of error of ±5% they are statistically the same.14
Resurrection of Jesus
Belief in the death, burial, and resurrection of Jesus Christ is deeply affirmed as described in Charts 6 and 7, but a low percentage of old-earth creationists doubt the resurrection. With young-earth creationists 0% dispute that Jesus died by crucifixion and 0% dispute that Jesus rose from the dead after three days. There is no doubt for young-earth creationists on these two central doctrines. This is slightly contrasted with old-earth creationists of whom 3% dispute that Jesus died by crucifixion and 9% dispute that Jesus rose from the dead after three days. For a majority of old-earth creationists there is no doubt that Jesus died, but there is some doubt with a minority that he rose from the dead.
Reported Miracles in the Old Testament
Belief in the reported miracles of the Old Testament is strongly affirmed as described in Charts 8, 9, 10; however, a small percentage of old-earth creationists do have some doubts. With young-earth creationists 0% dispute Jonah and the whale/fish account, 0% dispute Daniel and the lion’s den account, and 0% dispute that Moses parted the Red Sea and Israel walked on dry ground. There is no doubt among young-earth creationists that these accounts were accurately recorded true events. This is moderately contrasted with old-earth creationists of whom 12% dispute Jonah and the whale/fish account, 11% dispute Daniel and the lion’s den account, and 14% dispute that Moses parted the Red Sea and Israel walked on dry ground. Averaging the percentages together, 12% (about 1/8th) of old-earth creationists doubt these miraculous events reported in the Old Testament.
Six Literal 24-hour days in Genesis
Belief that God created the earth in six literal 24-hour days is strongly affirmed as described in Chart 11, but a smaller percentage of old-earth creationists do have some doubts. With young-earth creationists 5% dispute God created the earth in six literal 24-hour days. This is moderately higher for old-earth creationists of whom 14% dispute God created the earth in six literal 24-hour days.
Historical Adam
Belief that Adam and Eve were real people is affirmed as described in Chart 12; nevertheless, both groups demonstrate a moderately high belief that humans evolved from ape-like creatures (Chart 14). Within young-earth creationists, 0% dispute the historicity of Adam and Eve, and 18% believe humans evolved from ape-like creatures. This is almost statistically the same for old-earth creationists, of whom 5% dispute the historicity of Adam and Eve and 13% believe humans evolved from ape-like creatures. This finding presents a clear misunderstanding of young-earth creationism, because, by definition, a belief in the evolution of ape to man is not consistent with young-earth creationism. However, the purpose of the article is to argue that evolutionary science has influenced a segment of Florida Southern Baptists to doubt the inerrancy of the Bible. Even those who would align themselves with young-earth creationism have capitulated to a degree, maybe unknowingly, in the supremacy of science over the supremacy of the Bible.
Age of the Earth
The fact that 13% of young-earth creationists believe that science has influenced them to believe the earth is millions or billions of years old (Chart 15) is significant, but the above response to the historical Adam data should be a sufficient response. Of all the possible explanations, that 41% of those who claim to be young-earth creationists and believe dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago (Chart 13) is the most difficult to answer. A few possible responses exist, however. Response one is that 41% of those who believe that dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago and believe that the earth is less than 12,000 years old are really not young-earth creationists (Chart 1). This would then indicate that there is a greater percentage of old-earth creationists than those who self-identified as such within the Florida Southern Baptist convention; moreover, there is a greater proportion that have been influenced by evolutionary science. The data then might indicate through statistical analysis that belief in the age of the earth is a more significant cluster factor in belief in the inerrancy of the Bible; however, this potential analysis is beyond the scope of this article. Response two is that those 41% do reflect true young-earth creationists who have not pondered deeply this topic. However, if instructed with the implications of such belief and educated in a seminar from Answers in Genesis, the results might be significantly different. Response three is that, like seminary professors who affirm both the doctrine of inerrancy and hold to an old-earth cosmology,15 these are young-earth creationists who are inconsistent in their beliefs. However, unlike seminary professors, these lay persons have not realized that evolutionary science has influenced them to believe incongruous statements.
Of those who are old-earth creationists, 82% of them believe dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago (Chart 13), and 68% believe that science has influenced them to believe the earth is millions or billions of years old (Chart 15). Old-earth creationists still affirm inerrancy, even though they are more consistent in their beliefs about the age of the earth and dinosaurs; nonetheless, they are significantly more influenced by evolutionary science.
Noah’s Flood
Belief in the account of the Noah’s Flood is strongly affirmed, but a small percentage of old-earth creationists have doubts about the details. Within young-earth creationists, 0% dispute (Chart 16) there was a global Flood, and 1% dispute (Chart 17) that Noah and his family were the only human survivors. There is no doubt among young-earth creationists as to the historicity of Noah’s Flood. This is moderately contrasted with old-earth creationists, of whom 14% dispute (Chart 16) there was a global Flood and slightly contrasted with the 9% who dispute (Chart 17) that Noah and his family were the only human survivors. The responses from old-earth creationists show that a small percentage give allegiance to the supremacy of evolutionary science rather than the supremacy of the Bible.
Second Coming
Belief in the Second Coming of Jesus is deeply affirmed (Chart 18). Given the margin of error both groups affirm at the 100% mark that Jesus is returning.
Bible is Authoritative
Belief in the Bible as the final authority in one’s life is strongly affirmed for young-earth creationists, but much less for old-earth creationists (Chart 19). With young-earth creationists 5% believe homosexual marriage is biblically acceptable (Chart 20), 3% believe abortion is acceptable (Chart 21), 16% believe living with a boy/girlfriend is acceptable (Chart 22), and 20% believe a Christian marrying a non-Christian is acceptable according to the Bible (Chart 23). This increases with old-earth creationists of whom 12% believe homosexual marriage is biblically acceptable (Chart 20), 16% believe abortion is acceptable (Chart 21), 34% believe living with a boy/girlfriend is acceptable (Chart 22), and 52% believe a Christian marrying a non-Christian is acceptable to the Bible (Chart 23). The responses of both groups reveal that there is theological drift (significantly much more from old-earth creationists) from the belief in the authority of the Bible.
Spiritual Disciplines
Those who believe in young-earth creationism (80%) compared to old-earth creationism (66%) are more likely to attend church at least once a week (Chart 25). Compared to old-earth creationists over twice as many young-earth creationists (33% vs. 13%) attend church two times a week (Chart 26). As to Bible reading, a larger percentage of young-earth creationists (55% vs. 42%) read their Bible at least two times per week compared to old-earth creationists (Chart 27). One may wonder if belief in the age of the earth is really the influencing factor on Bible reading and church attendance. It would seem doubtful. Rather the increase of corporate worship and Bible reading would seem to reflect a greater likelihood that Florida Southern Baptist Church members would affirm the plain meaning of Genesis and be more likely to be exposed to teaching on Genesis. On the whole, both groups demonstrate inconsistent theological views, considering that they strongly affirmed a belief in the inerrancy of the Bible.
Summary of the Data
In general, there is a strongly held belief by young- and old-earth creationists that the Bible is the inerrant Word of God. Both affirm a belief in the doctrine of the Trinity, resurrection of Jesus, reported miracles in the Old Testament, supernatural events in Genesis 1–11, and believe the Bible is their final authority. However, a dissonance resides inside of this general belief between the supremacy of the Bible and the supremacy of evolutionary science. A greater influence of evolutionary science exists among those who affirm an old-earth view; nevertheless, those who affirm a young-earth view reveal that they, too, have been influenced by evolutionary science. About 18% of old-earth creationists question the inerrancy of the Bible compared to less than 1% of young-earth creationists. Roughly 8% of old-creationists doubt Jesus rose from the dead compared to 0% of young-earth creationists. On average about 12% of old-earth creationists doubt the miraculous events reported in the Old Testament compared to 0% of youth-earth creationists. As to historicity of Adam, young-earth creationists (100%) and old-earth creationists (95%) do believe he was real. However, surprisingly 18% of young-earth creationists believe humans evolved from ape-like creatures, while only 13% of old-earth creationists affirm this belief. The age of earth question was not consistently answered by young-earth creationists with 41% believing the dinosaurs lived on the earth millions of years ago compared to 82% of old-earth creationists. Of old-earth creationists, 14% dispute Noah’s Flood was global compared to 0% of young-earth creationists. In the area of biblical authority, old-earth creationists were more likely to affirm homosexual marriage (12% vs. 5%), abortion (16% vs. 3%), boy/girlfriend living together (34% vs. 16%), and a Christian marrying a non-Christian (52% vs. 20%) as acceptable. Finally, young-earth creationists were more likely to attend church at least once a week (80% vs. 66%) and more likely to read their Bibles two times or more per week (55% vs. 42%).
Theological Reflections
Factors that contribute to this inconsistency of affirmation in the doctrine of inerrancy are a belief (or disbelief) in the deity of Christ, supernatural events in Genesis 1–11, authority of the Bible for personal living, a general affirmation of inerrancy, and church attendance and Bible reading. All of these factors are interrelated and, particularly as one reflects upon the significance of Genesis 1–11, are the foundational chapters of the Bible. All of the supernatural events in Genesis are one-time occurrences. They cannot be known through sense perception. The existing data can be observed through reading the Bible, but the interpretation of the data is dependent upon the presupposition of the reader. Similarly, the virgin birth or resurrection of Jesus is not testable. If scientific data is allowed to influence the orthodox understanding of these two events (virgin birth and resurrection), then, over time, the belief in both will be dismissed because evolutionary science cannot prove it. This research would suggest thus that Genesis 1–11 be viewed through the same hermeneutical lens as the virgin birth and resurrection of Jesus. That is, believers affirm a young earth, not because dogma requires, but because Genesis 1–11 teaches it (much like the Trinity is implied).
Conclusion
Within the Florida Southern Baptist convention, there is a declared belief in the inerrancy of the Bible suggesting that a large percentage actually affirm this doctrine. When asked probing questions regarding various historical events and the authority of Scripture, however, a large percentage do not actually affirm inerrancy through their functional beliefs. The data suggest that some beliefs are more compatible with supremacy of evolutionary science than with supremacy of the Bible. There is a self-referentially incoherent belief among a significant percentage of Florida Southern Baptist Church members concerning the origins of life, science, miracles, and the authority of the Bible. This dissonance is best explained when a cluster of factors are considered: deity of Christ, supernatural events in Genesis 1–11, authority of the Bible for personal living, a general affirmation of inerrancy, and Church attendance and Bible reading. The intent of this article was to highlight the cluster factors of belief (or disbelief) in Genesis 1–11 and the influence upon the doctrine of inerrancy. May this research provide pause to those who devalue the significance of evolutionary science and its influence upon the doctrine of inerrancy of the Holy Scriptures.
References
Beemer, B. 2011. America’s Research Group. Retrieved from http://www.argconsumer.com/about.html.
Bush, L. R., and T. Nettles. 1999. Baptists and the Bible. Rev. Exp. Su. Nashville, Tennessee: B&H Academic.
Florida Baptist Convention. 2013. FBC Statistics. Retrieved from http://www.flbaptist.org/about-us/florida-baptist-state-convention/fbc-statistics/.
Garrett, J. L. Jr. 2009. Baptist theology: A four-century study. Macon, Georgia: Mercer University Press.
Geisler, N. L., and W. C. Roach. 2011. Defending inerrancy: Affirming the accuracy of Scripture for a new generation. Grand Rapids, Michigan: Baker Books.
James, G. 1986. Inerrancy and the Southern Baptist Convention. Dallas, Texas: Southern Baptist Heritage Press.
Leedy, P. D., and J. E. Ormrod. 2004. Practical research: Planning and design. 8th ed. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Report of the SBC Peace Committee. 1987. Report of the Southern Baptist Convention Peace Committee. In SBC Annual, item 153, pp. 56, 232–242. Retrieved from http:// www.baptist2baptist.net/b2barticle.asp?id=65.
Roach, D. 2010. HOW OLD? Age of Earth debated among SBC scholars. Florida Baptist Witness. Retrieved from http:// www.gofbw.com/news.asp?ID=12220.
Southern Baptist Convention. 2013. About the Southern Baptist Convention. Retrieved from http://www.sbc.net/aboutus/default.asp.
Sproul, R. C. 1996. Explaining inerrancy. Orlando, Florida: Ligonier Ministries.
Torbet, R. G. 1963. A history of the Baptists. Valley Forge, Pennsylvania: Judson Press.
Williams, R. 2000. The role of the Peace Committee in the Southern Baptist Convention inerrancy controversy. Cordova, Tennessee: Mid-America Baptist Theological Seminary. Available from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database. (UMI No. 9989310)
Wooddell, J. D. 2007. The Baptist faith and message 2000: Critical issues in America’s largest protestant denomination Ed. D. K. Blount and J. D. Wooddell. Kindle DX edition.
Appendix 1. Total Variance Explained
| Factor | Initial Eigenvalues | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 11.527 | 26.807 | 26.807 | 5.151 | 11.980 | 11.980 |
| 2 | 4.619 | 10.743 | 37.550 | 3.679 | 8.556 | 20.536 |
| 3 | 3.026 | 7.038 | 44.588 | 3.582 | 8.330 | 28.866 |
| 4 | 2.085 | 4.848 | 49.436 | 3.018 | 7.019 | 35.886 |
| 5 | 1.896 | 4.409 | 53.845 | 2.116 | 4.922 | 40.807 |
| 6 | 1.541 | 3.584 | 57.429 | 2.083 | 4.843 | 45.650 |
| 7 | 1.383 | 3.215 | 60.645 | 2.064 | 4.799 | 50.450 |
| 8 | 1.318 | 3.065 | 63.710 | 1.789 | 4.159 | 54.609 |
| 9 | 1.116 | 2.594 | 66.304 | 1.335 | 3.105 | 57.714 |
| 10 | 1.067 | 2.481 | 68.785 | .881 | 2.048 | 59.762 |
| 11 | .983 | 2.287 | 71.072 | |||
| 12 | .898 | 2.089 | 73.161 | |||
| 13 | .868 | 2.018 | 75.180 | |||
| 14 | .834 | 1.939 | 77.119 | |||
| 15 | .692 | 1.608 | 78.727 | |||
| 16 | .669 | 1.556 | 80.283 | |||
| 17 | .645 | 1.499 | 81.782 | |||
| 18 | .603 | 1.403 | 83.185 | |||
| 19 | .574 | 1.335 | 84.521 | |||
| 20 | .529 | 1.229 | 85.750 | |||
| 21 | .510 | 1.187 | 86.937 | |||
| 22 | .475 | 1.105 | 88.042 | |||
| 23 | .453 | 1.054 | 89.095 | |||
| 24 | .439 | 1.020 | 90.115 | |||
| 25 | .404 | .941 | 91.056 | |||
| 26 | .378 | .879 | 91.935 | |||
| 27 | .377 | .877 | 92.811 | |||
| 28 | .323 | .750 | 93.561 | |||
| 29 | .294 | .684 | 94.245 | |||
| 30 | .279 | .649 | 94.894 | |||
| 31 | .252 | .585 | 95.479 | |||
| 32 | .236 | .548 | 96.028 | |||
| 33 | .218 | .506 | 96.534 | |||
| 34 | .210 | .487 | 97.021 | |||
| 35 | .199 | .463 | 97.484 | |||
| 36 | .192 | .446 | 97.931 | |||
| 37 | .173 | .402 | 98.332 | |||
| 38 | .164 | .382 | 98.714 | |||
| 39 | .154 | .357 | 99.071 | |||
| 40 | .131 | .305 | 99.377 | |||
| 41 | .105 | .245 | 99.621 | |||
| 42 | .090 | .209 | 99.830 | |||
| 43 | .073 | .170 | 100.000 | |||
Appendix 2. Rotated Factor Matrix.
| Factor | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| Q17 | .805 | |||||||||
| Q18 | .793 | |||||||||
| Q19 | .782 | |||||||||
| Q20 | .714 | |||||||||
| Q23 | .677 | .301 | ||||||||
| Q24 | .492 | .485 | .357 | .323 | ||||||
| Q12 | .457 | -.326 | .354 | |||||||
| Q8 | .436 | |||||||||
| Q27 | .356 | .865 | ||||||||
| Q26 | .335 | .818 | ||||||||
| Q25 | .345 | .773 | .302 | |||||||
| Q28 | .397 | .598 | .346 | |||||||
| Q34 | .338 | .334 | ||||||||
| Q33 | ||||||||||
| Q37 | .886 | |||||||||
| Q38 | .864 | |||||||||
| Q40 | .782 | |||||||||
| Q62 | .512 | |||||||||
| Q11 | .344 | -.469 | -.411 | |||||||
| Q50 | .391 | |||||||||
| Q36 | .376 | .353 | ||||||||
| Q1 | .801 | |||||||||
| Q4 | .330 | .697 | ||||||||
| Q2 | .489 | |||||||||
| Q7 | -.466 | |||||||||
| Q49 | .369 | |||||||||
| Q57 | -.607 | |||||||||
| Q59 | .555 | |||||||||
| Q44 | .462 | |||||||||
| Q46 | -.384 | |||||||||
| Q53 | ||||||||||
| Q31 | .827 | |||||||||
| Q32 | .692 | |||||||||
| Q41 | .301 | -.529 | .372 | |||||||
| Q35 | .323 | .767 | ||||||||
| Q39 | .735 | |||||||||
| Q58 | -.438 | .439 | ||||||||
| Q3 | .349 | |||||||||
| Q65 | .835 | |||||||||
| Q64 | .773 | |||||||||
| Q45 | .322 | .755 | ||||||||
| Q13 | .415 | .315 | .455 | .315 | ||||||
| Q14 | .376 | .428 | ||||||||
Extraction Method: Maximum Likelihood.
Rotation Method: Varimax with Kaiser Normalization.a
a. Rotation converged in nine iterations.